Proper Workstation Positioning – Computer Desk Ergonomics

In an era where technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, it is crucial to recognize the significance of maintaining good ergonomics while using computers.
The ramifications of a poor working position and bad ergonomics are far-reaching. Improperly adjusted chairs, desks, monitors, and keyboards can lead to discomfort, musculoskeletal disorders, and even long-term health issues.
Here, we will thoroughly discuss the fundamentals of good workstation ergonomics, offering expert advice (suggested by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) to help you create an ergonomic workstation, maintain good habits that support your health, and enhance your overall computer work performance at computer workstations.
We also have an industrial ergonomics training course that you should also look at.
Ergonomic Workstation: The Essentials
In this section, we’ll provide valuable insights into proper ergonomics and practical tips to help you create a workspace that promotes health and enhances performance.

Maintain a Neutral Position
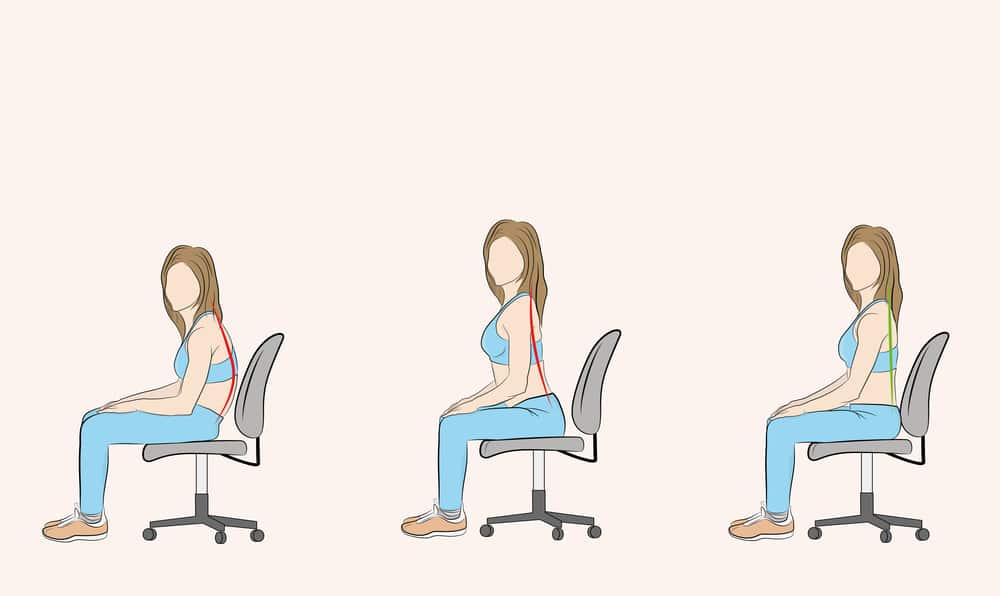
Achieving neutral positioning is a key principle in creating an ergonomic workstation that promotes comfort and reduces the risk of musculoskeletal issues. Neutral positioning refers to aligning your body in a natural and balanced posture that minimizes strain on your muscles, joints, and tendons.
While this might sound complicated to achieve, neutral positioning can easily be obtained by making few minor changes to your current positioning habits while sitting at your desk.
Start by adjusting your chair’s seat depth so your feet are flat on the floor or supported by a footrest. Keep your knees at a 90-degree angle, and your thighs parallel to the floor – this ensures proper circulation and reduces the risk of discomfort or swelling in your legs.
Next, focus on your backrest. Position it to support the natural curve of your spine, particularly in the lower back region. This helps distribute your body weight evenly and alleviates stress on your back muscles. You may want to consider using a lumbar support cushion if your chair lacks sufficient back support.
Lastly, don’t forget about your posture – sit upright with your shoulders relaxed and your head in line with your spine. Avoid slouching or hunching forward, as this can strain your neck and back muscles, and regularly remind yourself to check and correct your posture throughout the day.
Feet Flat on the Floor
One often overlooked aspect of maintaining a correct position is ensuring your feet are flat on a surface. By keeping your feet rested flat, you actively contribute to maintaining a balanced and stable posture, which helps alleviate the strain on your lower back, hips, and legs.
It’s a simple yet effective way to reduce the risk of discomfort and potential musculoskeletal disorders arising from sitting at a desk for prolonged periods, such as lower back pain or stiffness.
Keep Your Keyboard at Arm’s Length
Maintaining your keyboard at arm’s length is paramount to minimize strain on your wrists, upper arms, and shoulders. Positioning your keyboard too far away may cause you to overreach, leading to unnecessary strain on your muscles and tendons.
On the other hand, placing it too close may force you to hunch forward, resulting in a poor sitting posture and increased pressure on your neck and shoulders.
To find the ideal distance for your keyboard, start by sitting back in your chair with your back fully supported. Extend your arms comfortably in front of you and parallel to the floor, allowing your elbows to rest in a relaxed position at your sides.
The keyboard should be within easy reach, enabling you to type without stretching or straining your arms or shoulders. Be sure to keep frequently used objects (cell phones, pens, mice, etc.) at arm’s reach.

Place Your Monitor at Eye Level
When creating an ergonomic workstation, one of the most critical factors to consider is the positioning of your monitor. Whether your monitor is a laptop screen or a regular detached monitor, you might unknowingly strain your neck and eyes by placing the monitor too high or too low.
If your current setup doesn’t allow you to adjust your monitor or laptop screen to your desired height, consider using a laptop stand or an adjustable arm to elevate or lower your screen accordingly. This allows for easy customization to suit your individual needs and reduces eye strain.
Use a document holder to keep necessary papers at eye level while you type, and wear bifocals if needed.
Take Breaks Throughout the Day
Neglecting to take regular breaks throughout the day can have serious consequences for your health and productivity. Incorporating short, frequent breaks into your work routine is vital to maintaining an ergonomic workstation.
Why are breaks so important? Well, when you sit or engage in repetitive tasks for extended periods without rest (such as sitting on your computer workstation all day), your muscles become fatigued, and your concentration and performance levels can suffer.
Prolonged sitting can lead to full-body stiffness, reduced blood circulation, and increased spinal disc pressure, contributing to back and neck pain. Take regular breaks to stand up or go for a short walk.
Consider Using a Wrist Rest
A wrist rest is a padded support in front of your keyboard and provides a cushioned surface for your wrists and hands. This pad helps maintain a more neutral position for your wrists, reducing strain and preventing discomfort, such as wrist pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and repetitive strain injuries. Industrial ergonomics can certainly help reduce these types of injuries.
Using a wrist pad can alleviate the pressure on your wrists while typing or using your mouse, allowing for a more relaxed and ergonomic hand position. It serves as a supportive buffer that encourages proper alignment and prevents your wrists from resting directly on a hard surface.
Proper Working Positions
While sitting upright and standing straight is often hailed as the epitome of good posture, the truth is that there’s more to proper working positions than a rigidly straight back.
Embracing a range of ergonomic adjustments and postures can provide flexibility, comfort, and improved well-being. In this section, we’ll explore alternative working positions that can reduce strain on your body while working at computer workstations.
Standing Posture
Standing up occasionally is a fantastic remedy to ensure your muscles, feet, neck, and elbows don’t stiffen throughout the day. Standing at your desk is one position that may be your best bet if you need to switch up the routine for your legs and arms for a while.
In this position, it is crucial to align your legs, torso, neck, and head in an imaginary vertical line, with your feet slightly apart for stability. You could also use a footrest to elevate one foot while standing.
Avoid slouching or leaning excessively forward or backward while standing up, as these positions can strain your back, neck, and shoulders over time. Adjust your mouse, laptop, desk height, or keyboard tray if necessary.

Reclined Sitting Posture
When adopting the reclined posture, your upper body, neck, and head should form a vertical alignment while slightly leaning back at an angle ranging from 105 to 120 degrees relative to your thighs. Think of this as an ergonomic alternative to slouching at computer workstations.
This slight recline lets you sit comfortably and helps distribute the weight more evenly throughout the body, reducing pressure on specific areas and alleviating strain on the muscles and joints.
Declined Sitting Posture
A more active variant of the reclined posture, a declined posture, calls for your thighs to be inclined, with your buttocks slightly elevated compared to your knees.
The angle between your thighs and torso should always be greater than right angles while your torso remains vertical or slightly reclined. The legs, on the other hand, should be positioned vertically.
To achieve a declined sitting posture that promotes optimal ergonomics, ensure that your chair does provide support for your lower back and promotes a natural curve in your spine. The backrest should be slightly reclined, providing stability while allowing you to maintain good posture.
The most important thing to remember is always to find the right balance between comfort and functionality. Always adjust your desk height, tilt, and the position of your keyboard and monitor to align with your sitting posture.

Proper Workstation Positioning: Final Thoughts
Good computer ergonomics are vital for maintaining a healthy and productive work environment.
By following Occupational Safety and Health Administration-approved ergonomic guidelines, you can prevent the development of discomfort and pains associated with prolonged computer use.
Remember to prioritize factors such as correct chair height, monitor positioning, keyboard, and mouse placement, and take regular breaks to optimize your well-being and enhance your work performance.
FAQ
To set up computer workstations, adjust your chair to a comfortable height with your feet laid flat. Place your computer monitor directly in front of you, at eye level (use a stand if necessary), and keep your keyboard, desk, seat, and mouse at a height that allows your arms to repose comfortably.
Ensure proper lighting and regular breaks to maintain good posture and prevent strain.
When sitting at computer workstations, be sure to follow these Occupational Safety and Health Administration-approved guidelines for good posture and ergonomics:
1) Sit with your feet resting flatly on the floor.
2) Maintain a neutral spine, with your back supported by an ergonomic chair that provides lumbar support.
3) Ensure your monitor is at eye level.
4) Keep your elbows at a 90-degree angle and your wrists straight.
1) Ensure that your desk height allows for your elbows to be at a 90-degree angle when typing, and adjust your desk positioning in a way that allows for proper alignment of your monitor, keyboard, and mouse, reducing strain on your neck, head, and body.
2) Ensure enough space to move and adjust your chair comfortably.