OSHA Confined Space Training Requirements by Role

OSHA Confined Space Training Requirements by Role
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.146(g) requires employers to provide training to employees before assigning them to work in permit-required confined spaces. 29 CFR 1926.1207 outlines confined space training requirements specifically for construction. While many best practices align, general industry employers should rely primarily on 1910.146.
The OSHA definition of a confined space is as follows:
- The space has limited or restricted means of entry and exit.
- The space is not designed for continuous human occupancy.
- The space is large enough for people to enter fully and perform work.
Permit-required confined spaces like manholes, tanks, and silos may contain or have the potential to contain hazards to the worker, include material that can engulf the employee, or could trap the employee inside, along with other health and safety hazards.
If employees must enter the space like this on site, OSHA requires employers to develop a written permit space program and to train employees on best practices. The program must cover, among other topics, identifying and controlling hazards, using and maintaining PPE, calling for rescue services, and training employees on their assigned roles. Specific training requirements depend on the employee’s role and responsibilities in the confined space.
In this post, we will cover confined space definitions, roles and duties of the employer and employee, and training requirements to help employers stay compliant with OSHA standards.
If you need help with training, we offer a confined space training course that includes everything you need to certify employees in-house, including presenter’s notes, a PowerPoint, video, quiz, and more.

Which Employees Must Receive Confined Space Training?
If your employee has to access confined spaces for work, OSHA requires you to designate their roles, identify their duties, and provide them with the necessary safety training. Regulations identify four positions in confined space work, each with different responsibilities and training requirements.
- Entrant: A person whom the employer has authorized to enter a permit space
- Attendant: A person stationed outside the permit space who monitors entrants and performs other assigned duties
- Entry supervisor: The person (such as the employer or crew chief) responsible for determining whether conditions are acceptable for entry, authorizing entry, overseeing entry operations, and terminating entry
- Rescue Personnel: Properly trained and equipped personnel available for emergencies requiring confined space rescue
Entry supervisors may also serve as attendants or entrants as long as they have the proper training and equipment.
If no one can enter the confined space to work, employers must prevent entry by posting warning signs that detail the existence, location, and danger of the space.
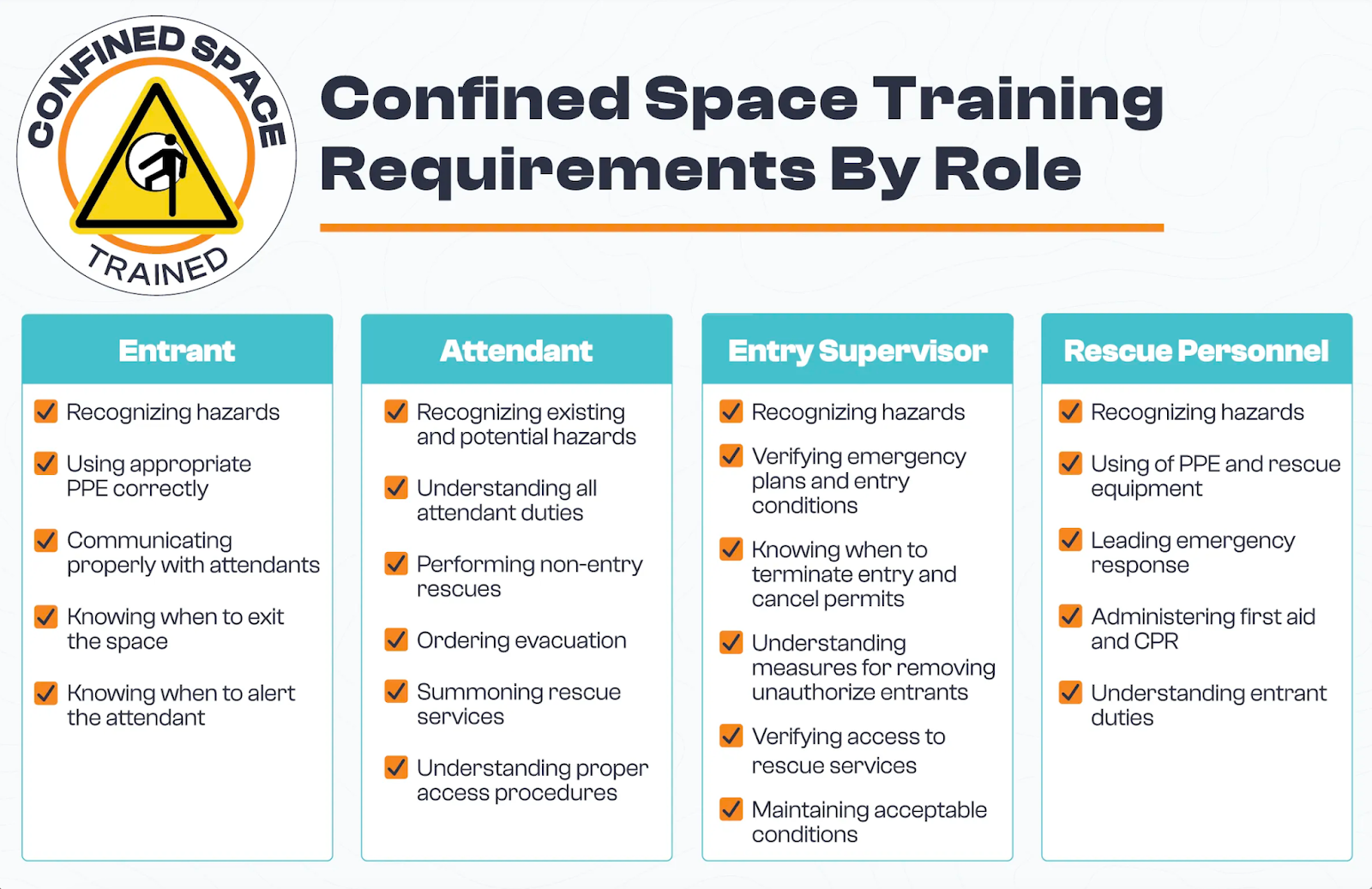
What Must Confined Space Training Cover?
Per OSHA 1910.146, employers must provide training so that all employees working with confined spaces have the understanding, knowledge, and skills to safely perform their duties.
A qualified person, which is anyone that has extensive knowledge and experience, can provide training.
The exact type of training each employee needs will depend on their role.
Training for Authorized Entrants
Authorized entrants must be proficient in the following:
- Recognizing space hazards, including the means, symptoms, and consequences of exposure
- Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) correctly
- Communicating properly with attendants
- Knowing when to exit the confined space
- Knowing when to alert the attendant of dangerous or prohibited conditions
Training for Attendants
Attendants must be proficient in the following:
- Recognizing existing and potential hazards, including the mode of exposure, signs or symptoms, consequences, and physiological effects
- Performing non-entry rescues
- Ordering the evacuation of a permit space
- Summoning rescue services in an emergency
- Proper access procedures (e.g., ensuring that unauthorized people do not enter the confined space and reporting cases of unauthorized entry)
- Attendant duties (e.g., remaining outside the confined space during entry operations and not performing other work that interferes with their primary duties)
Training for Entry Supervisors
Entry supervisors must be proficient in the following:
- Recognizing space hazards, including the mode, signs, and consequences of exposure
- Verifying emergency plans and entry conditions before allowing entry
- Knowing when and how to terminate entry and cancel permits
- Appropriate measures for removing unauthorized entrants
- Verifying the availability and accessibility of rescue services
- Maintaining acceptable entry conditions and ensuring that operations remain consistent with the permit
Training for Rescue Personnel
Rescue personnel must be proficient in the following:
- Understanding the hazards of confined spaces
- Using personal protective and rescue equipment
- Responding to emergencies promptly
- Performing assigned rescue duties
- Administering first aid and CPR (including one team member with current certification)
- Authorized entrant duties (must receive entrant training)
In many cases, the training for each role will overlap. For example, rescue personnel must also go through authorized entrant training, and employers can also combine training for entrants and attendants.
Employers should also make sure other employees working near the site understand what to do in an emergency. Even if it’s not required by OSHA 1910.146, anyone who works near confined spaces can benefit from awareness training for safety purposes.
Training Documentation Requirements
OSHA 1910.146 requires employers to document the successful completion of required confined spaces training. Employers must retain the record of employee training and make it available for inspection by employees or their authorized representatives. Certification must contain the following:
- The employee’s name
- The trainer’s signatures or initials
- The training dates
What Our Confined Space Training Package Includes
You can use our safety videos to streamline your training program. Specifically, our Confined Space Training covers everything your employees will need to know, from atmospheric testing and PPE to implementing a permit space program and designating an entry team.
Purchasing our training programs provides the following benefits:
- Full compliance: We’ve researched the relevant OSHA guidelines to create our training programs, so you don’t have to.
- Complete package: Along with the safety video, you’ll get a presenter’s guide, trainee quizzes and sign-in sheets, and certificates of completion to make training easy and hassle-free.
- Flexible options: Just need one video? Purchase a single training course on a USB stick or DVD for just $239. Prefer access to our entire library? Choose an annual online subscription!
Several of our other videos also cover confined space requirements, including the following:
- HAZWOPER Confined Space Entry Training
- HAZWOPER Exposure Monitoring and Medical Surveillance
- HAZWOPER Monitoring Procedures Training
- Testing and Monitoring for Hazardous Gases
- Anhydrous Ammonia Safety

Does Confined Space Training Expire?
Unlike some standards, OSHA 1910.146 does not require a specific timeframe for retraining or training renewal. Instead, OSHA stipulates that employers must train or retrain employees working in permit spaces if the following circumstances apply:
- Before the employee begins relevant job duties
- Before the employee has a change in assigned duties
- When a change in operations presents a new hazard not covered by the employee’s previous training
- When the employee shows deficiencies in their knowledge or use of proper procedures
OSHA does have two time-specific requirements related to confined space operations. These include:
- Employers must review their written permit program annually.
- Employee rescue personnel must perform practice rescue services annually.
Fortunately, training and retraining are affordable and easy with our safety videos. You can have your employees watch our Confined Space Training program as many times as they need: when you begin new operations, when you update your confined space program, or when you need to rectify inadequacies in an employee’s entry procedure.
Do Employers Need to Train Contractors?
While host employers are not required to provide training to contractors, they must ensure coordination. This includes informing contractors about:
- The permit space entry requirements
- Identified hazards and the employer’s experience with the space
- Precautions or procedures to follow in or near the space
The employer must also advise that permit space entry is only allowed through adherence to an OSHA-compliant permit space program, coordinate entry operations, and debrief the contractor at the conclusion of entry operations.
How to Identify Permit-Required Spaces
Permit-required confined spaces have one or more of the following hazards:
- Atmospheric hazards: The space contains or potentially contains toxic gases, vapors, or fumes, such as carbon monoxide or hydrogen sulfide. These kinds of hazards are typically found in confined spaces underground, such as manholes.
- Physical engulfment: The space contains material such as dirt, grain, or liquids that could potentially engulf an entrant. These types of hazards can be found in confined spaces like silos or tanks.
- Dangerous configuration: The space has walls converging inward or floors sloping downward and tapering into a smaller area that could trap or asphyxiate a worker.
- Other hazards: The space contains some other recognized serious safety or health hazards, such as unguarded machinery, exposed electrical components, dangerous animals, or extreme temperatures.
If the confined space does not meet the definitions as stipulated in 1910.146(b), then the OSHA standard on confined spaces does not apply. Instead, employers should consult other applicable standards.
If you’re unsure whether you must follow the requirements in 1910.146 for permit-required confined spaces, OSHA provides a workflow to help employers assess their workplace. In addition, our Confined Space Training video covers how to keep your workers safe and stay OSHA compliant by including how to differentiate permit and non-permit spaces, how entry permits work, and what employees must know about working safely in various types of confined spaces.
Common Permit-Required Confined Spaces by Industry
Many employers and employees are left wondering what type of area constitutes a confined space per OSHA regulations. To answer these questions, the OSHA Confined Spaces Advisor provides a list of common confined spaces by industry. Below are some examples of confined spaces found across various industries in the United States.
- Bins
- Boilers
- Conveyor enclosures
- Diked areas
- Dust collectors
- Furnaces
- Hoppers
- HVAC systems
- Mixers
- Pits
- Precipitators
- Sewers
- Silos
- Tanks
- Tunnels
- Vats
- Vaults
- Vessels
Each industry also has confined spaces common to that specific industry. For example:
- Agricultural operations: Confined space hazards in this industry would include feed grinders, manure/bio-digester units, silage dump wagons, and environmentally controlled produce storage units.
- Food production: This industry’s confined spaces include bleachers, heated liquid sugar bins, hydrogenators, kettles, protein bins, and tallow tanks.
- Chemical products: Confined spaces in an industry that relates to chemistry could include cyclones, fermentors, spray dryers, and waste recovery tanks
- Transportation equipment manufacturing: Confined spaces in these industries include aircraft spaces, chip/coolant pits, prefueled/postfueled wing tanks, and test chambers.
Keep in mind that the applicable OSHA standard may vary by industry. OSHA 1910.146 is the confined space standard for general industry, establishing the broad requirements for permit-required spaces.
However, it does not apply to construction, shipyard, or agricultural employment, which have specific requirements in standards 1926 Subpart AA (Construction) and 1915 Subpart B (Shipyard). While OSHA 1910.146 may not apply to some industries like agriculture, it still serves as a general guide to prevent accidents in and around confined spaces.
Keep Your Workplace Safe with Confined Space Entry Training
From cave-ins and toxic gases to extreme temperatures and dangerous animals, confined spaces can pose a number of threats to your workers. By administering the proper training to your employees, you’ll not only protect your staff from a hazardous work area but also protect your company by preventing accidents and expensive OSHA fines. Contact us today for more information about our OSHA-compliant confined space training videos.