Whose Responsibility Is It to Provide and Pay For PPE?

Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a fundamental component of workplace safety and is responsible for protecting workers from potential hazards.
Once a workplace hazard assessment has been conducted, employers must implement a comprehensive PPE program that lists the required equipment for each task on the job site.
Who is responsible for paying for PPE? And who is responsible for paying for that PPE?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires employers in the construction industry and beyond to provide PPE for their employees. Employers who fail to comply with OSHA’s safety standards may be required to pay heavy fines.
Keep reading to learn more about the employer payment requirement for personal protective equipment and the OSHA standards about required PPE for various industries. Also, we do have a PPE Training Video if you need full Personal Protective Equipment training for your employees.

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): An Overview
Personal protective equipment includes all safety gear that protects an employee from workplace hazards.
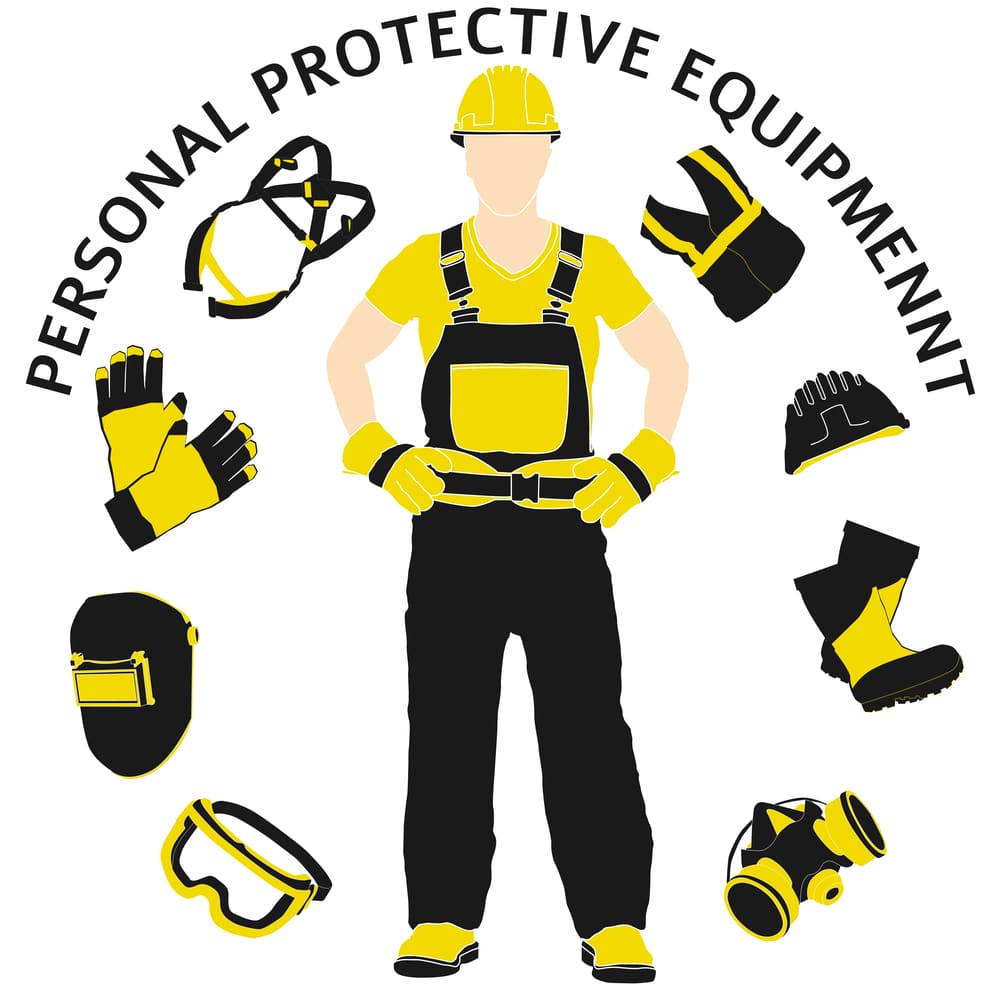
Common examples of personal protective equipment include:
- Safety glasses and other eye protection
- Protective gloves such as nitrile or rubber gloves
- Fall protection equipment
- Hearing protection
- Respiratory protection
- Hard hats
- Face shields
- Safety shoes and other foot protection
Other PPE may be required for more niche roles on the job site.
Proper protective equipment is an indispensable element of a safe working environment. However, it is considered the last line of defense against workplace hazards. All employers must implement targeted engineering and administrative controls to protect employees and ensure everyone’s safety.
So whose responsibility is it to provide appropriate PPE?
Who Is Responsible for the Purchase of PPE?
Who takes responsibility for PPE? In most cases, it’s the employer.
Under OSHA regulations, the employer is required to pay for PPE any time their employees may be exposed to hazards at work that could cause illness or injury.
OSHA has established guidelines regarding the maximum exposure limits for various substances in the work area. Any employer failing to protect their employees from hazardous materials must pay heavy fines and may face legal consequences as well.

What Does PPE Cost?
Here’s a table with average costs of various kinds of PPE:
| PPE Item: | Cost Range in U.S. Dollars $: |
| Safety Glasses | $5 to $45 |
| Hard Hats | $15 to $55 |
| Safety Gloves | $10 to $40 |
| Hearing Protection | $5 to $75 |
| High Visibility Vest | $10 to $25 |
| Steel-Toe Boots | $50 to $150 |
| Respirators | $20 to $50 |
| Face Shields | $15 to $30 |
| Coveralls | $20 to $50 |
| Knee Pads | $10 to $35 |
| Safety Harness | $50 to $250 |
| Cut-Resistant Sleeves | $10 to $25 |
| Flame-Resistant Clothing | $50 to $200 |
| Chemical-Resistant Gloves | $15 to $35 |
| Disposable Dust Masks | $3 to $17 |
| Welding Helmets | $50 to $150 |
| Ear Muffs | $15 to $60 |
| Rubber Boots | $20 to $50 |
These are approximate ranges, and actual prices may fall outside these ranges. However, this does give you an idea of what employees are paying for the PPE worn by employees.
When Should Employees Provide Their Own PPE?
There are two main types of PPE employers are not expected to provide: safety-toe protective footwear and prescription safety glasses.
However, even when employees provide their own PPE, it is the employer’s responsibility to ensure everyone has the right PPE for the task at hand and the hazards present in the workplace.
Employers must also ensure that all employee-owned PPE is kept in good working order and that any worn-out equipment is promptly repaired or replaced.
Finally, the employer is responsible for training workers on the correct use and maintenance of personal protective gear.
Why Must Employers Provide Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)?
Employers are responsible for protecting their employees and ensuring their safety in the workplace. No employee should be exposed to unsafe working conditions or dangerous materials without adequate protection.
Appropriate protective gear is a cornerstone of a safe working environment, which is why it’s imperative that employers pay for all employee PPE.
Let’s review some specific reasons why employers must equip their workers with the necessary PPE for their jobs.
Protect Employees
Every employer has an obligation to protect workers from hazards in the work area.
Any employee working with hazardous substances, dangerous machinery, or in a potentially unsafe environment should wear the necessary PPE to mitigate any potential injury or illness caused by those hazards.
Prioritizing employee safety by providing PPE helps create and maintain a safe and productive working environment.
Employees who are outfitted with the gear they need to stay safe at work have a higher opinion of their workplaces and are more likely to stay at their jobs than those who feel their safety is disregarded.

Mitigate Risks
Workplaces across all industries come with inherent risks to employee health and safety. These hazards can cause injury, illness, and other negative health effects that affect workers’ abilities to do their jobs.
Employers have a practical and legal obligation to protect their workers from these risks by providing essential protective equipment.
Employees who are injured on the job may be entitled to workers’ compensation and could bring expensive lawsuits against the employer. It’s simpler (not to mention cheaper) to pay for PPE than to risk OSHA fines and costly litigation.
Employers also lose revenue when their employees are unable to work due to decreased productivity in the work area.
Finally, an employer who fails to protect their subordinates from dangers in the work area will be faced with a loss of morale, which can lead to walkouts and high turnover.
Comply with OSHA Standards
Established by Congress in 1970, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) monitors worker safety in the United States and mandates that employers in all sectors protect their workers from any dangers in the work area.
OSHA requires employers to provide PPE to their employees and may impose fines and other sanctions on any employer that fails to do so.
What If the Employer Can’t Acquire the Correct PPE?
If the employer cannot acquire the specific PPE for their industry as outlined in OSHA Standard 1926.28, it is responsible for providing an adequate replacement.
The costs of protective equipment may be daunting, especially for small businesses with limited budgets.
But again, it’s ultimately much cheaper to budget for protective equipment than to suffer the fines, legal fees, and other expenses that can result from neglecting worker health.
OSHA Regulations and Personal Protective Equipment
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) holds employers responsible for protecting their workers and requires employers to provide personal protective equipment to all employees. OSHA Standard 1926.28 covers the specifics of employer accountability with regard to PPE.
All new employees must receive PPE before they start working. The equipment must be properly fitted and inspected to ensure it provides sufficient protection.
Remember that while employees are responsible for providing some types of personal protective equipment (such as safety-toe protective footwear and prescription safety glasses), employers must still ensure their workers have the proper PPE for their given jobs and that all gear on the work site is in good working order.
OSHA also requires employers to train their workers on the proper use of their safety gear.
Required PPE by Industry
OSHA requirements for protective equipment differ by industry according to the types of hazards at each site.
The exact type of PPE required isn’t always specified; OSHA outlines the working conditions that necessitate protective equipment. The employer is then required to acquire the appropriate gear to address and mitigate those risks.
Let’s cover the employer payment requirement for each industry, including the types of PPE employers are responsible for providing.
General Industry
Since “general industry” is a catch-all term for all industries outside the construction, agriculture, and maritime sectors, its PPE requirements vary widely.
OSHA mandates that employers provide hearing protection any time workers may be exposed to sustained sounds measuring over 85 decibels.
Breathing apparatuses must be provided if there are contaminants in the air within the work zone.
Eye protection is required for workers exposed to gases, dust, harsh chemicals, and other airborne particles that could irritate or damage the eyes.
Laboratories and other workplaces with clean rooms must be outfitted with full-body suits. These suits must be regularly cleaned and serviced to ensure they remain airtight and sterile.
Construction Industry
Since there are more on-the-job deaths within the construction industry than in any other industrial sector, OSHA standards for construction industry PPE are more stringent and specific than for other industries.
Employers working in construction must pay for the following types of gear for their employees:
- Head protection such as hard hats
- Welding helmets
- Eye protection such as safety glasses or face shields
- Boots or safety shoes
- Fall protection equipment
- Protective gloves
Fall protection is one of the most crucial pieces of protective equipment within the construction industry. According to OSHA, 65% of contractors working in construction work at heights, and falls are the leading cause of death in the industry.
Maritime Industry
Shipyard employment presents many unique dangers that can adversely affect worker health and safety.
OSHA lists the following types of PPE as required depending on the specific task being performed:
- Welding helmets
- Fall protection equipment, including harnesses, lanyards, and personal arrest systems
- Hard hats and other head protection
- Safety glasses or goggles
- Hearing protection
- Face shields or breathing protection (if working with caustic chemicals or eye irritants)
Agriculture Industry
Employees in the agricultural industry are frequently exposed to hazardous chemicals, and many work daily alongside dangerous equipment.
PPE for these workers can include:
- Face shields
- Breathing apparatuses
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
- Aprons
- Sturdy footwear
OSHA’s regulations single out eye protection as the most important PPE for agriculture workers. Employers are required to pay for safety glasses and/or goggles for their employees.

PPE and Occupational Safety: Final Thoughts
Personal protective equipment (PPE) serves to protect employees from hazards at work and ensure the safety of everyone on the team.
Providing PPE and paying for it is one of the employer’s biggest responsibilities. Failure of responsible employers to provide sufficient PPE can result in heavy fines from OSHA.
As an employer, ensuring your workplace complies with OSHA standards is to your benefit. Pay for and provide PPE for every employee on your payroll to maintain a safe and successful work environment.