Is HACCP a Voluntary Process? – [Updated for 2023]

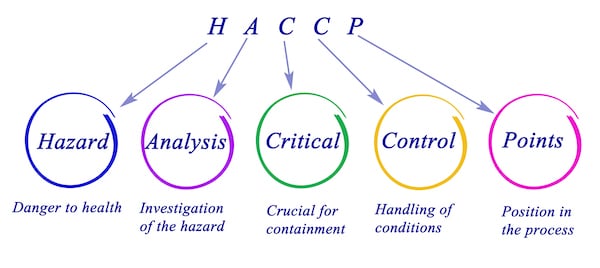
When you go out to a restaurant or order takeout, you most likely don’t think too much about getting food poisoning. This is because the HACCP system is designed to keep consumers and food operators safe. HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis Critical Points of Control.
With a plan like this in place at your favorite restaurant, you can enjoy your meal without having to worry about getting sick. The only catch is that not every food establishment follows the HACCP food safety management system. Some food handlers and food service businesses don’t have HACCP Training in place, and don’t follow those guidelines. But, there is a good reason why some businesses follow this food safety practice and some don’t…
Keep reading to learn more about food safety rules and whether HACCP is a voluntary process or not.
What is Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points?
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points is also knows as HACCP. It’s an internationally recognized system for preventing food safety hazards from occurring during food production processes, but it remains a voluntary process for most food businesses in the United States.
These are a set of standards that promote public food safety. The HACCP management system protects consumers and workers from food-borne hazards, like listeria, shigella, and salmonella that can start and spread in a food prep environment.
HACCP standards require that food handlers follow established hygiene rules for preparing food, inspecting raw materials, and handling raw materials and chemicals. These standards are designed to prevent hazards from occurring. This includes the following:
- Biological hazards
- Chemical hazards
- Physical hazards
Is HACCP Mandatory or Is HACCP a Voluntary Process?
To answer the question, “Is HACCP a voluntary process or a mandatory process?”, the short answer is that it is voluntary.
In the United States, HACCP is not mandatory. It’s a voluntary process that leaves the ultimate responsibility of whether to follow the guidelines or not up to individual food handlers. This process differs from other food safety systems because it puts more responsibility on those who implement the guidelines. It adds pressure on anyone involved with the development process to the implementation and success of the management system.
Why Is HACCP a Voluntary Process?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) only require mandatory HACCP programs for juice, meat, and poultry. Although it’s a voluntary process, its use is highly recommended for safe food handling. Having a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points plan also prevents issues like food fraud.
Although the FDA only requires HACCP plans for some food groups, companies that fall under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) are required to have a written Food Safety Plan (FSP). The FDA guidelines endorse the voluntary implementation of this plan in retail and all food service establishments, but the responsibility is ultimately up to the owners.
However, food safety laws in the UK require all food businesses to follow a mandatory HACCP food safety plan. This became a law because of EU regulation centered on the hygiene of food related services.
Is HACCP a Voluntary Process Until There’s a Health Hazard?
We’ve established that HACCP is a voluntary process. Although it’s not mandatory to have a fully-fledged HACCP system, each plan protects public health. HACCP systems remain a voluntary process even when problems are discovered.
A HACCP plan would decrease these risks during services but, as long as FDA and USDA guidelines, there is no requirement to begin following this voluntary plan. Food business operators should work with regulatory authorities and health inspectors to ensure food is safe.
HACCP is a voluntary process, but not only does it reduce the risks of foodborne illness, it:
- Reduces product loss
- Increases product quality
- Creates better control over product inventory
- Promotes consistency in product preparation
- Increases profits
- Increases employee awareness
Food Safety
HACCP is a voluntary plan, but it is not a stand-alone program. One of the biggest benefits of its employment is preventing problems from occurring. It’s better than standing-alone proactive food safety standards because workers don’t have to wait until a health hazard occurs to keep the environment safe.
The main goal of the program is to control the most critical areas of any food production environment to ensure that all food is safe for consumption. There are three major health hazard categories: biological hazards, chemical hazards, and physical hazards.
Keep in mind that the hazards included in a HACCP plan are only for those that can cause illness or injury. More is being done to incorporate the system into other areas of the food industry, including catering.

Biological Hazards
Biological risks are responsible for most foodborne illnesses during the production and distribution processes. The distribution of these illnesses is one of the greatest concerns to inspectors. They include:
- Disease-causing bacteria
- Viruses
- Parasites
- Mold
- Yeast
- Natural toxins
Chemical Hazards
Chemical risks put the health of consumers and workers at risk when they come in contact with food. They include:
- Pesticides
- Machine oil
- Cleaning solutions
- Sanitizers
- Dissolved metal
- Excessive food additives
Physical Hazards
Physical risks are objects that should not be included in food handling or raw material production. Physical dangers from raw material production or other parts of the food handling plan can cause injury when eaten. They include:
- Glass or metal pieces
- Toothpicks
- Jewelry
- Cigarette butts
- Hair
Food Safety Management System
How is HACCP a voluntary process? It’s used to identify any form of hazard that can occur when handling food. The HACCP process involves identifying and evaluating the flow of foods through the establishment to determine the points of critical control.
Core HACCP Principles
The FDS promotes the voluntary process of a HACCP system to effectively control foodborne illness risk factors. HACCP is a voluntary process, but each business should have an official plan for its services to protect customers and workers through each step of production.
Seven core principles guide the HACCP system. Below are the HACCP seven food safety management principles integrated with routine business operations to guarantee food safety.

Hazard Analysis
This step involves evaluating the current operation and identifying potential hazards. Expertise is required to make an accurate evaluation of any hazards in the environment by prerequisite programs and the HACCP plans. This means a trained professional must carry out the two steps that make up hazard analysis.
The first part is identifying any form of hazard and the second part is evaluating them. Once identified and evaluated, the critical control points must be identified. These points determine where a hazard needs to be controlled to prevent creating a risk.
Identify Critical Control Points
This step requires asking what controls can be applied to stop or eliminate hazards that have been identified during the hazard analysis step. For each critical point that is identified, a preventative measure needs to be taken. This can include a change in temperature, time, procedures, etc.
Establish Critical Limits
The next step establishes the criteria for the critical points. This can include creating a minimum and maximum limit for temperature, pH, salt level, etc. If the limits are ever exceeded, corrective action needs to be taken to prevent a health hazard from occurring.
Establish Monitoring Procedures
Monitoring the critical control points is essential for keeping the HACCP process effective. The monitoring procedures are made up of measuring and observing things that can be done promptly so action and control can be taken to prevent a production situation.
Establish Corrective Actions
This is where the actions that need to be taken are established if a critical limit is not met. Action needs to be taken to ensure the finished product is safe. The production flow also needs to be evaluated to determine and eliminate the cause of the problem.
Establish Verification Procedures
The HACCP plan has to be validated. The plan in place needs to be effective in preventing and identifying all hazards. The finished product should be tested to verify that the controls are working as expected.
Establish Record Keep and Document Procedures
The establishment decides what records and documents are necessary to show that the HACCP plan is being followed and that the system is in control. Always include records of the development and operation of the system.
Conclusion
HACCP stands for hazard analysis critical control points. Although HACCP is not a mandatory process, it’s extremely important for safe food handling. Just a few minutes are needed to make any changes to the current plan or form one.
HACCP is a voluntary process and isn’t a zero-risk system, but it decreases the possibility of hazards to an acceptable level. Having a HACCP certification makes it easier to show off a business to customers and makes the establishment a safer environment for everyone.