What Are the Benefits of an HACCP Program? [Updated in 2023]

If you run a restaurant, bar, factory, or other food and beverage-related business, you’re likely profoundly familiar with the importance of food safety management. Food hygiene is an essential part of operating a successful business in the industry, as is staying up-to-date with all food safety laws in your community. Further, getting an HACCP training video can help your business stay on the cutting edge of food safety by keeping your employees trained.
It can only take one case of customer food poisoning to turn a thriving establishment into a failed restaurant. Nothing loses a food business money faster than complaints, citations, and fines related to poor food handling. Fortunately, health hazards due to poor food hygiene can be easily avoided by implementing quality management systems such as an HACCP plan.
Keep reading to learn all about HACCP implementation to ensure a safe and legal business, including how HACCP compliance benefits your business and how HACCP training can improve your employees’ performance and morale.
What Does HACCP Stand For?
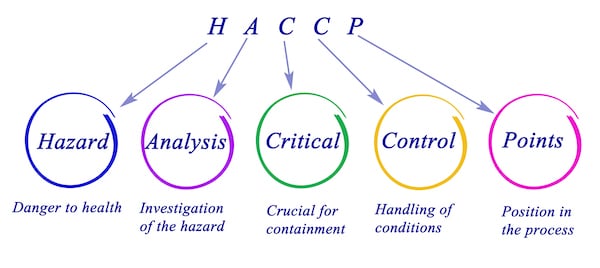
HACCP is an acronym for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point. At its core, an HACCP management system outlines and streamlines food safety standards, monitoring protocols, and standard operating procedures for businesses in the food industry in accordance with food safety acts.
An internationally recognized system, HACCP’s method has proven successful at preventing food contamination, reducing the risk of food-borne illness, and decreasing the prevalence of physical hazards due to lack of clarity around workplace safety procedures.
The FDA designed and tested the first HACCP systems in the 1960s, based on strategies implemented by NASA to test ways of preparing safe food for space missions. Since then, HACCP has enjoyed a standing as one of the foremost systems for preventing food contamination. One of the program’s hallmarks is its focus on teaching employees to value the importance of food hygiene.

Common Hazards Targeted by HACCP Plans
The food production process is rife with opportunities for chemical, physical, and microbiological contaminants to enter, particularly in facilities that handle raw materials. Salmonella, e. coli, and norovirus are three of the most common microbial contaminants found in food production facilities. At the same time, pesticides comprise a dangerous category of chemical contaminants that can make consumers of the contaminated product very sick.
Items are subjected to end-product testing that can catch these contaminants before the products reach consumers; however, this failsafe does not prevent the hazards from occurring in the first place, nor does it address the conditions that led to the contaminants entering the food.
HACCP plans introduce monitoring procedures that ensure HACCP-trained employees are aware of all the points where something could go wrong in the production process. With an HACCP system in place, employees will be on the lookout for anything that could constitute a potential hazard, and they’ll also know how to address problems that arise in a timely and efficient manner.
Which Aspects of the Food Industry Are Covered By HACCP Principles?
HACCP principles cover every stage of the food production process from harvesting to consumption, implementing food safety systems at every step along the food chain to ensure that all food produced is safe for human consumption. Farms, factories, restaurants, grocery stores, and caterers are all required to operate under HACCP guidance and can all benefit significantly from implementing an HACCP system.
HACCP-compliant companies are expected to ensure compliance across all aspects of their business, including within their supply chain. All employees should take food safety seriously and comply with all food handling and food hygiene guidelines as outlined by the HACCP plan.
What Are the Prerequisites for Implementing an HACCP System?
An HACCP plan should be built on the shoulders of other quality management systems such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) to be implemented successfully. Some examples of GMPs include pest control, cleaning and sanitation procedures, and control of all non-food biological, chemical, and physical agents in the facility.
Additionally, the company should already have a strong understanding of and adherence to the Codex Alimentarius General Principles of Food Hygiene, which describes the general guidelines in place for products meant to be traded internationally.
Before implementing the HACCP system, an HACCP team should be formed of personnel who have a deep understanding of HACCP principles and food safety. This team is then responsible for developing a flow diagram describing each step of implementing the new HACCP system in a straightforward, easily comprehensible way.
All employees within the facility should be educated on HACCP guidelines and have a thorough understanding of their exact role in upholding those guidelines. A reasonable amount of time should be given to this training, and employees must be provided with all tools, equipment, and materials necessary to complete their HACCP training and carry out the analysis and monitoring tasks assigned to them.

The Seven Principles of the HACCP System
As outlined by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), there are seven HACCP principles that must be followed to meet the requirements of HACCP compliance.
These seven principles are as follows:
1. Conduct a Hazard Analysis
During a food business hazard analysis, the HACCP team must assess all potential hazards. Any food safety hazard that could cause a serious problem if left unchecked will be recorded and analyzed, along with any physical hazards that could lead to injury among employees, customers, or other visitors to the facility.
2. Identify Critical Control Points (CCPs)
The next step for your HACCP team after completing the hazard analysis is identifying any critical control points (CCPs) along the food chain. A critical control point is a juncture at which control can and must be applied to prevent a food safety hazard or other potential hazards. Each critical control point is determined with an eye toward food safety management, with safe food and the highest possible food quality being the desired outcome.
3. Establish Critical Limits
Having identified the critical control points, the HACCP team must establish critical limits for each point that detail the minimum or maximum level of control necessary to prevent food safety hazards from occurring or reaching unacceptable levels. An example of setting a critical limit is determining raw materials’ acceptable temperature, appearance, or aroma during the food production process. Each critical limit must be scientifically-based and have at least one criterion for food safety derived from research, experts, and regulatory standards and guidelines.
4. Establish Monitoring Procedures
Next, a planned sequence of measurements and observations is established for all critical control points to assess whether the critical limits are being adhered to at each point. There are three major reasons why it is essential to monitor critical control points.
For one, monitoring is necessary for tracking food safety management because it will alert employees to a trend toward loss of control before a total deviation from the critical limit occurs.
Secondly, if deviation does occur, monitoring will allow employees to catch the problem and apply necessary corrective actions.
Finally, monitoring results in documentation is an integral part of verification procedures.
5. Establish Corrective Actions
While the HACCP system is designed to ensure food quality by eliminating as many potential hazards from the production chain as possible, there will sometimes be unavoidable or unforeseeable deviations from the plan that result in errors. Corrective actions must be developed in advance for each control point so that any errors that occur can be rectified as swiftly as possible, thereby preventing hazards from spiraling out of control.
6. Establish Verification Procedures
Verification encompasses all actions other than monitoring that reinforce the legitimacy and effectiveness of the HACCP plan and demonstrate that the plan is functioning to promote food safety and disease control.
7. Record Information
The final principle of the HACCP plan is to establish procedures for record-keeping and documentation. Records of the HACCP system should include the names and responsibilities of the HACCP team members, details about the critical control points, monitoring procedures, and corrective actions, along with descriptions of the products prepared onsite.
Benefits of HACCP Programs
From a safety standpoint, there are many benefits of HACCP system implementation for businesses in the food industry. However, an HACCP system can have several other benefits beyond food hygiene, such as improved employee morale, better customer retention, and a safer, more efficient workplace.
Prevent Food Safety Hazards
HACCP compliance among food industry businesses has been shown to significantly decrease the risk of food hazards, including lowering the chances of foodborne illness, chemical contamination, and physical contaminants.
Even a business that takes hygiene very seriously could find itself on the rocks if one of its suppliers has an outbreak. HACCP protects you by requiring each of your suppliers’ facilities to live up to the same rigorous standards in place at your business.
Meet Legal Obligations
Safe food is a top priority among lawmakers and consumers alike, and many laws relating to food safety are strictly enforced by government agencies such as the FDA and FSIS. Food products not certified by the FDA are not permitted to be sold in US markets, and food companies that do not abide by FDA and FSIS regulations are often subjected to heavy fines.
HACCP certification protects businesses by helping them meet the standards set by food safety laws. With an HACCP system in place, you won’t have to stay on top of every law that gets passed relating to food hygiene; you can rest easy knowing your food management system meets the standards set by top government agencies.

Protect You and Your Business
It only takes one disgruntled customer to tarnish a food business’s reputation forever. Suppose a customer gets sick after consuming your products and tries to bring litigation against your business. In that case, the documentation provided by your HACCP system can help make your case and save thousands of dollars in fines and legal fees for your company, not to mention protecting your reputation.
If a government health inspector visits your business, you’ll be able to show them your records and demonstrate your business’s due diligence in following internationally recognized food safety guidelines.
Implement a Standardized Food Production Process
Structure and organization are fundamental when it comes to multi-stage operations like food production. With the guidelines set in place by an HACCP system, you’ll find production can carry on more smoothly and efficiently because everyone knows exactly what their role is and how each stage of the production process should look.
HACCP guidelines also require rigorous adherence to specifically-outlined standards, which requires a high degree of teamwork and efficiency. Learning to work together as a team will boost your employees’ overall performance, increasing the productivity of your business.
Save Money in the Long Run
While the upfront costs of designing and implementing an HACCP program can be considerable, having a system in place for hazard analysis and food hygiene will save you money in the long run by protecting you from the legal fees and noncompliance fines that could be leveled at you without a food safety management system in place.
Boost Employee Morale
Most employees want to know they’re working for an employer who cares not only about their health and well-being, but also the health and well-being of the customers and the community. Many workers in the food industry are particularly dedicated to providing customers with a positive dining experience, and they want to work for an employer who shares that drive.
Knowing they’re working for a business that takes safety and hygiene very seriously will improve employee loyalty and confidence, allowing your employees to do their best work and thrive in their positions.
Improve Customer Retention
Consumers are more likely to patronize establishments that are clear and upfront about taking food safety seriously. Implementing a high-quality HACCP system at your business will demonstrate to your guests that their health and well-being are of the utmost importance to you, increasing the likelihood that first-time diners will return to your restaurant.
If your business is a factory, food supplier, or distributor, restaurants will be more likely to work with you if your facilities are neat, clean, and operating under HACCP guidelines.
Finally, since the HACCP system is recognized internationally as a thoroughly effective food safety plan, having your HACCP certificate will allow you to sell your food products in other countries.

Control Potential Hazards
Food-borne illness is a leading cause of disease in the United States and is often linked to businesses in the food industry that deal with raw material production. Raw meat, seafood, and leafy greens are all frequent culprits in outbreaks of food-related diseases.
In addition, all aspects of the food industry carry certain physical risks for their employees. Factories often have dangerous machinery and materials, and restaurants tend to be hectic, fast-paced work environments with many opportunities for dangerous errors.
Under an HACCP system, all of your employees will have a clear understanding of the risks involved in the work they’re doing, and everyone will be aware of the stages of production at which errors are most likely to occur. Additionally, employees will know which corrective actions to take if something goes wrong to prevent hazards from spiraling out of control.
How Much Does HACCP Certification Cost?
The cost of obtaining HACCP certification and implementing an HACCP system varies widely depending on a number of factors. For example, a small ice cream shop will find it easier and less expensive to set up a HACCP plan than a large factory with hundreds of employees might.
Businesses should budget for acquiring a certification and implementing a sound system. The budget should also accommodate the cost of renewals, as the license must be renewed annually.
This might sound expensive. However, since HACCP plans can save any food industry business money in the long run by lessening the risks of an expensive fine or lawsuit, certification costs are well worth paying for businesses of any size.
What is the Process for HACCP Certification?
After training employees in HACCP principles and setting up a company-wide HACCP plan, the next step in the certification process is an audit. An HACCP audit is an inspection carried out by a third-party authority that is legally qualified to assess the success and validity of your business’s HACCP system.
The auditor will need to conduct a thorough inspection of your physical facility, as well as examine all relevant documents and records.
The amount of time it takes to complete an HACCP audit varies depending on the size and scope of the business being audited. Generally speaking, the certification process will be complete after a period of one to five days.
HACCP certification must be renewed annually.
The Bottom Line
No business in the food production or restaurant industry can operate successfully without a rigorous plan in place for food safety management. There are too many variables at work to leave proper food handling up to chance, and even one blind spot in the food chain could have disastrous health and safety consequences down the line.
Under an HACCP system, you and your employees can work with the confidence that your facility meets all laws and guidelines relating to food hygiene and hazard management.